Introduction
Addiction rarely develops in isolation. For many people, substance use is not the core problem—but a coping response to unresolved trauma. Emotional wounds from childhood abuse, neglect, violence, loss, or chronic stress can silently shape behaviors, cravings, and relapse patterns. This is why trauma therapy plays a critical role in addiction recovery: it treats the cause, not just the symptoms.
Understanding the Trauma–Addiction Connection
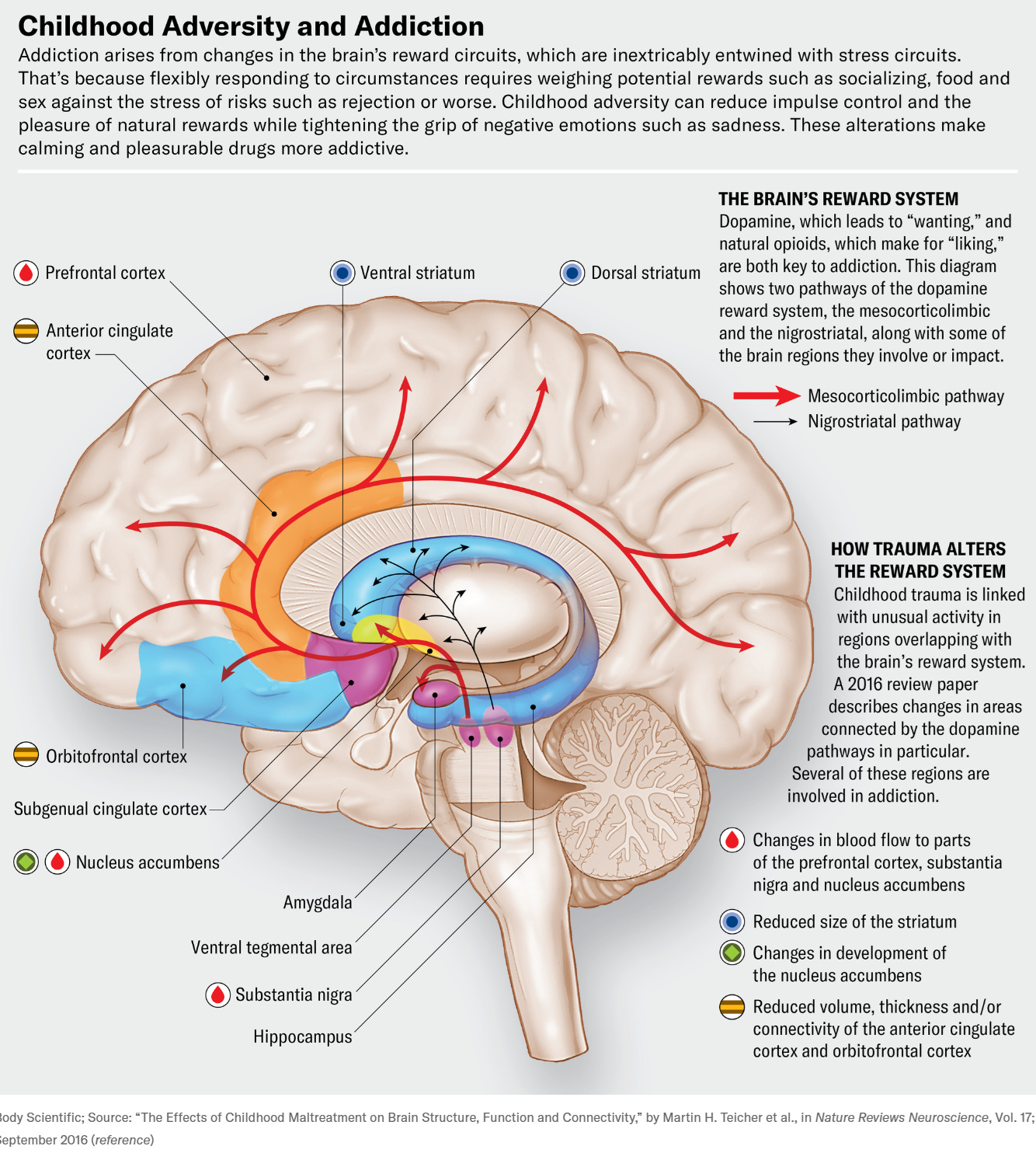
Caption: Trauma alters stress and reward systems in the brain, increasing vulnerability to substance use.
Trauma changes how the brain processes stress, emotions, and rewards. When trauma is unresolved:
-
The nervous system remains stuck in fight, flight, or freeze
-
Stress hormones stay elevated
-
Emotional regulation becomes difficult
-
Substances may feel like the fastest way to numb pain or feel “normal”
Over time, addiction becomes a learned survival strategy rather than a conscious choice.
Why Traditional Addiction Treatment Isn’t Always Enough
Many treatment programs focus on stopping substance use through detox, discipline, or behavioral control. While these steps are important, they may fail if trauma is ignored.
Without trauma therapy:
-
Emotional triggers remain unaddressed
-
Stress easily recreates cravings
-
Shame and self-blame intensify
-
Relapse risk stays high
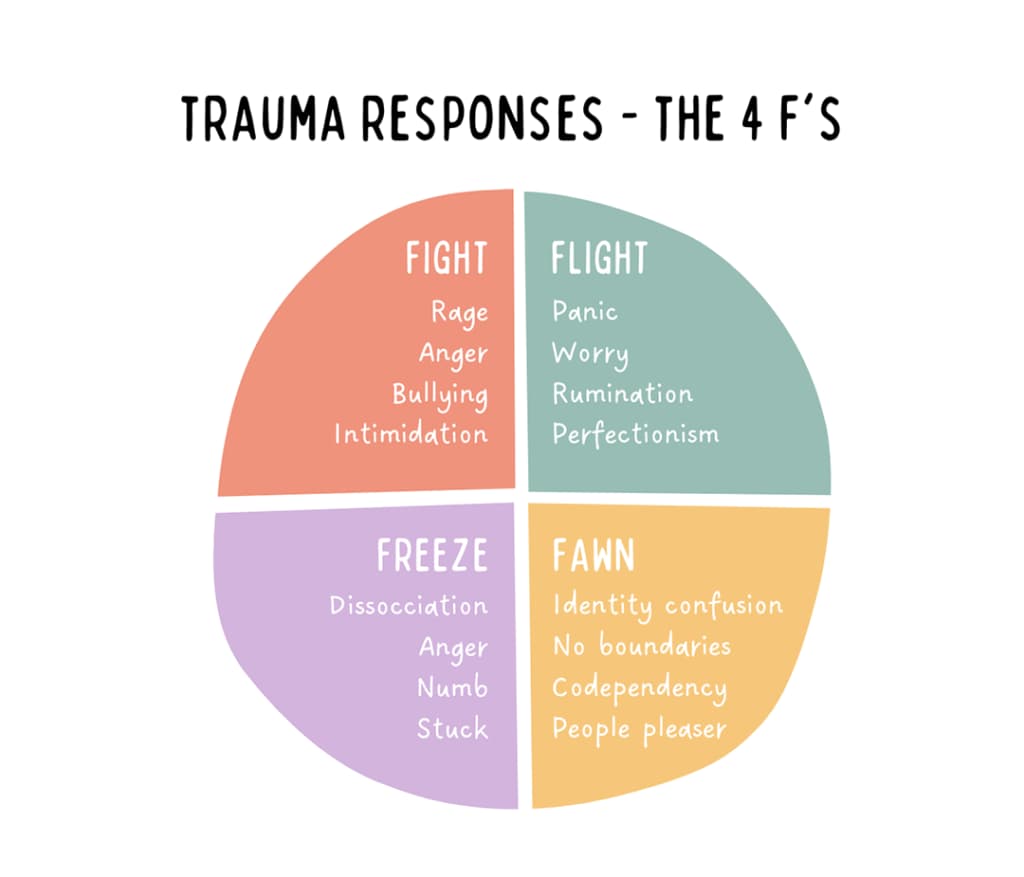
Trauma-informed care recognizes that relapse is often a trauma response, not a moral failure.
How Trauma Therapy Supports Recovery
Caption: Trauma therapy helps the brain and body feel safe again—without substances.
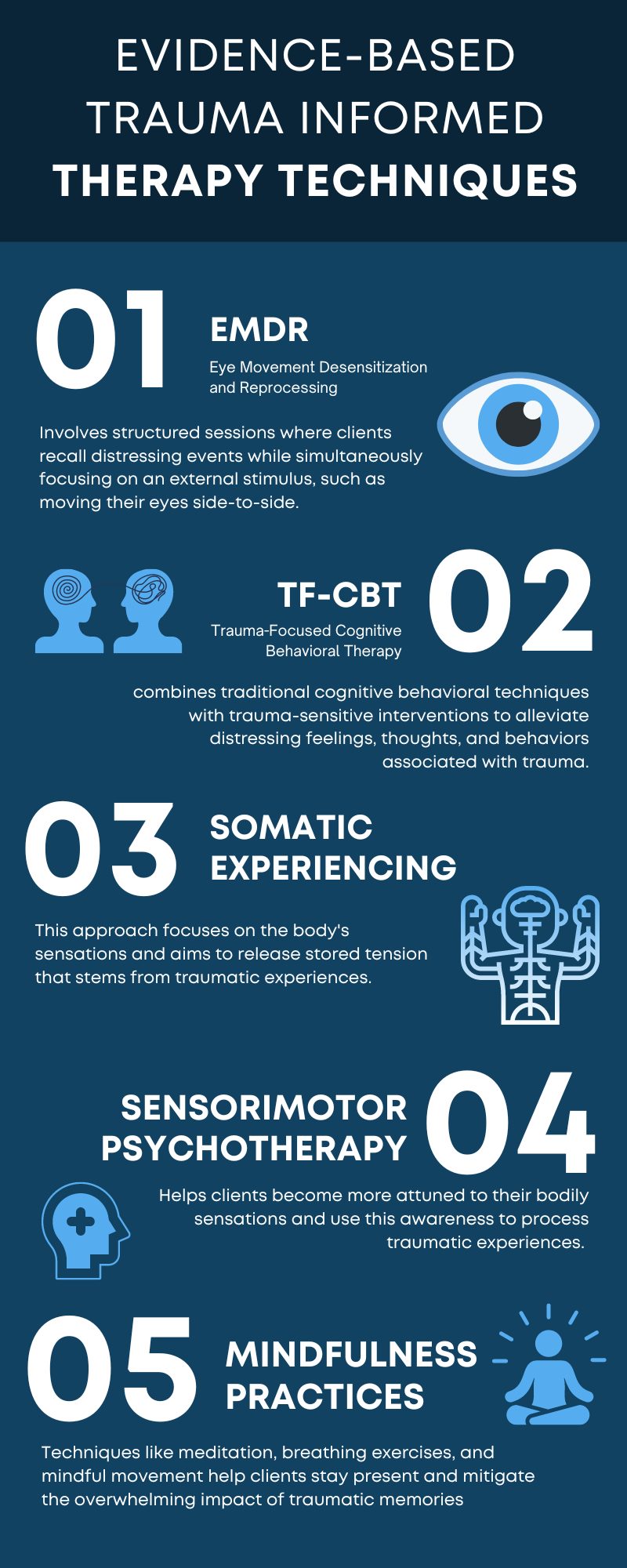
Trauma therapy works by gently helping individuals process painful experiences without becoming overwhelmed. Effective trauma-based approaches include:
-
EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing): Reduces emotional intensity of traumatic memories
-
Somatic Therapy: Releases trauma stored in the body
-
Trauma-Focused CBT: Reframes harmful beliefs rooted in past trauma
-
Internal Family Systems (IFS): Heals wounded inner parts driving addictive behavior
These therapies help people:
-
Regulate emotions without substances
-
Reduce automatic stress reactions
-
Build a sense of safety and self-trust
-
Replace survival coping with healthy strategies
Breaking the Cycle of Relapse
Caption: When trauma heals, triggers lose their power.
Unprocessed trauma often resurfaces during stress, loss, or conflict—moments when relapse risk is highest. Trauma therapy interrupts this cycle by:
-
Identifying trauma-based triggers
-
Teaching grounding and self-soothing skills
-
Rebuilding emotional resilience
-
Strengthening nervous system regulation
Recovery becomes less about “white-knuckling” sobriety and more about internal stability.
Healing Trauma Builds Long-Term Recovery
Caption: True recovery begins when pain is processed, not avoided.
Trauma therapy doesn’t erase the past—but it transforms how the past lives in the present. As trauma heals, people often report:
-
Fewer cravings
-
Improved emotional clarity
-
Stronger relationships
-
Greater self-compassion
-
A renewed sense of purpose
Addiction recovery becomes sustainable because it is no longer driven by unresolved pain.
Conclusion
Addiction is often a symptom of deeper emotional wounds. Treating trauma is not optional—it is essential for lasting recovery. Trauma therapy allows individuals to heal at the root, reclaim control over their nervous system, and build a life where substances are no longer needed for survival.
When trauma is healed, recovery becomes freedom—not a constant fight.