Introduction
Sleep is not simply a pause from waking life—it is one of the most active and essential periods for brain repair. While the body rests, the brain works intensely to heal, reorganize, and restore itself. From clearing toxic waste to strengthening emotional resilience, sleep is the brain’s most powerful recovery tool.
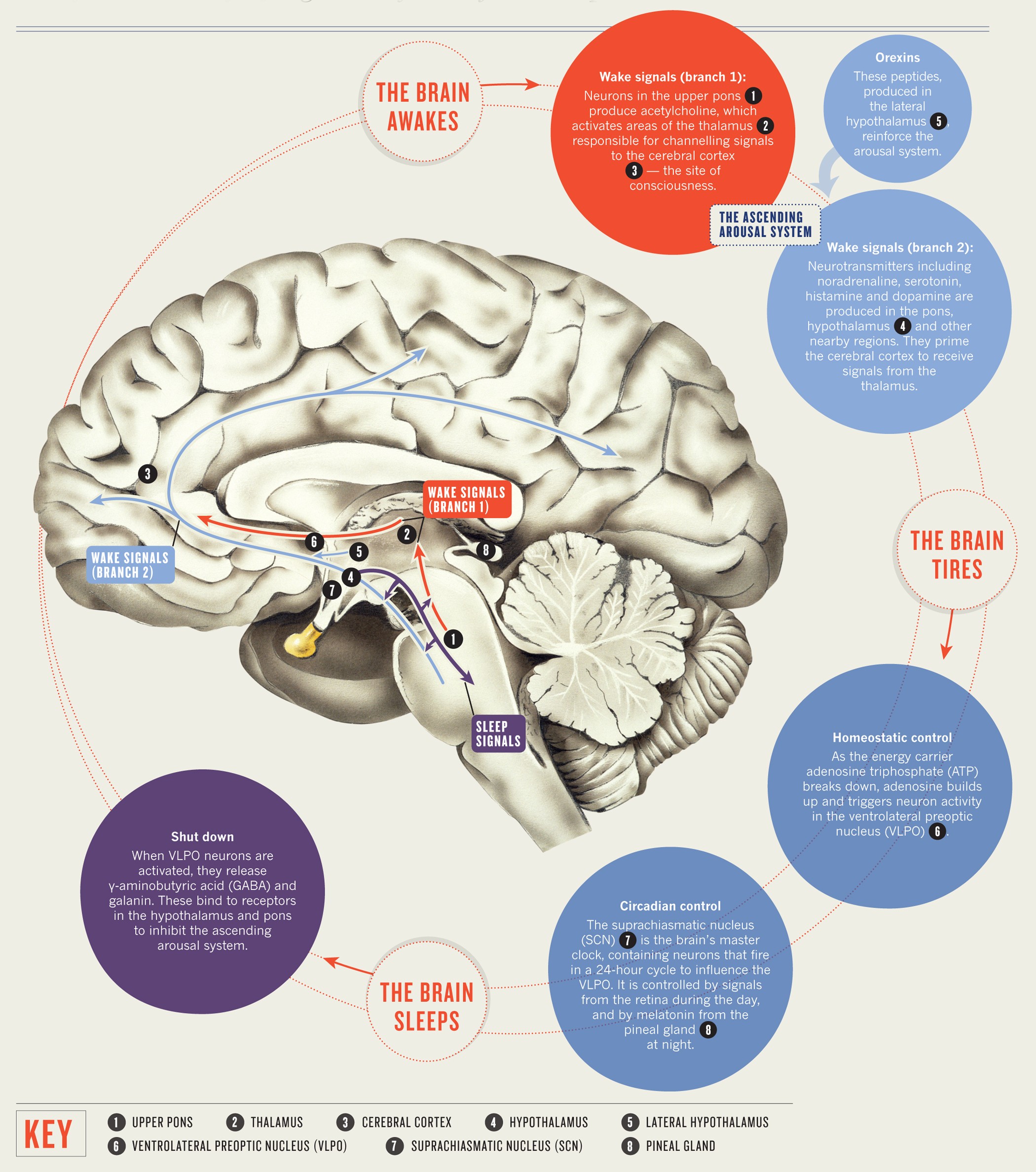
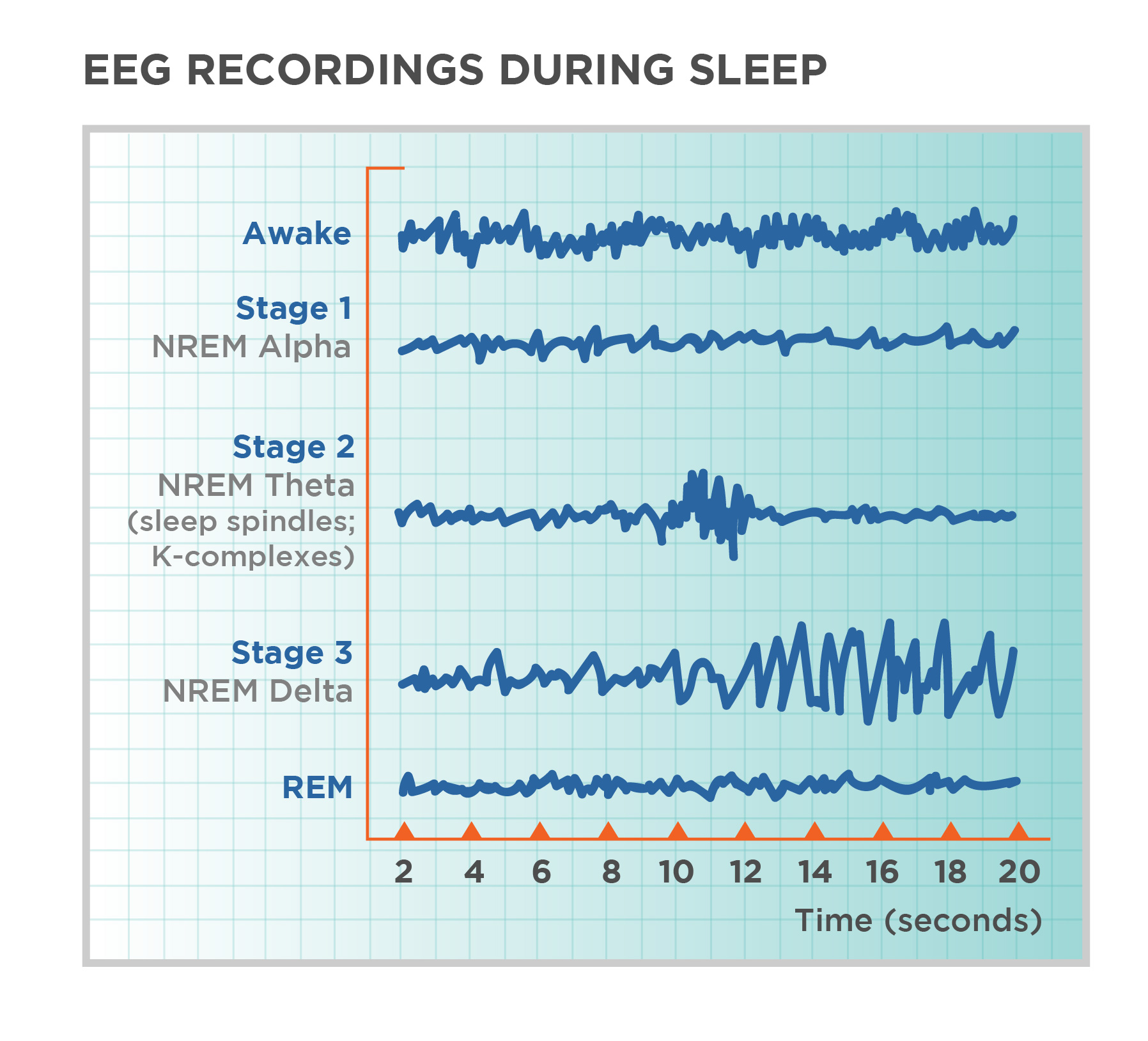
1. The Night Shift: What the Brain Does While You Sleep
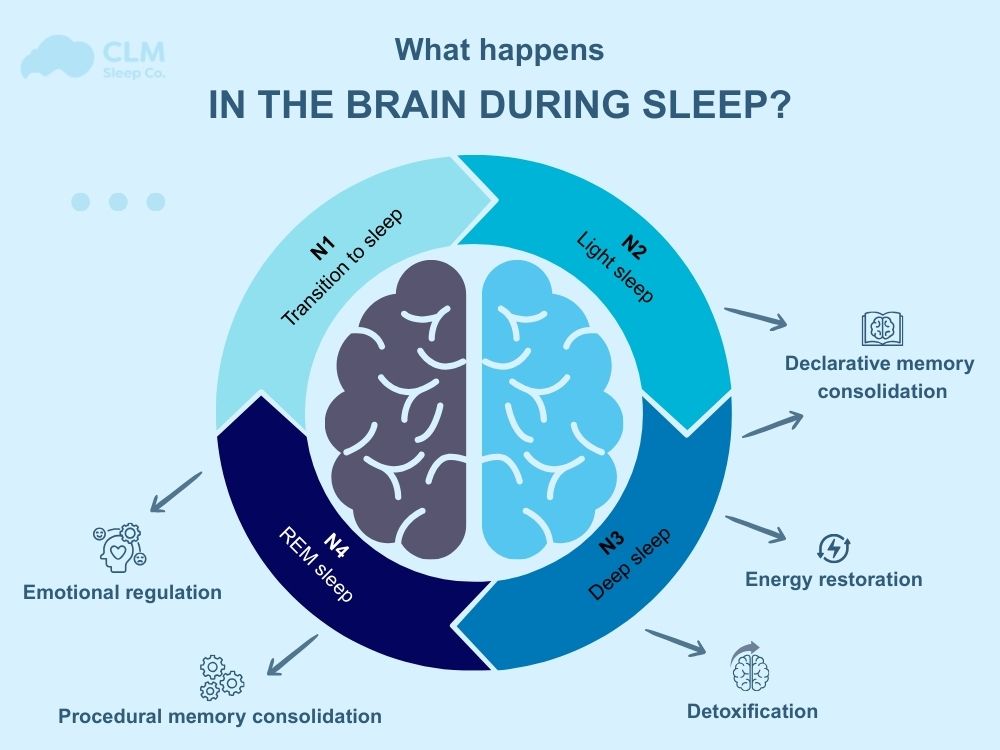
During sleep, the brain cycles through non-REM and REM stages, each playing a unique role in repair:
-
Deep non-REM sleep focuses on physical and neural restoration
-
REM sleep supports emotional regulation, creativity, and memory integration
Together, these stages allow the brain to recover from stress, learning overload, and emotional strain experienced during the day.
Image caption: The brain cycles through multiple sleep stages, each responsible for different repair processes.
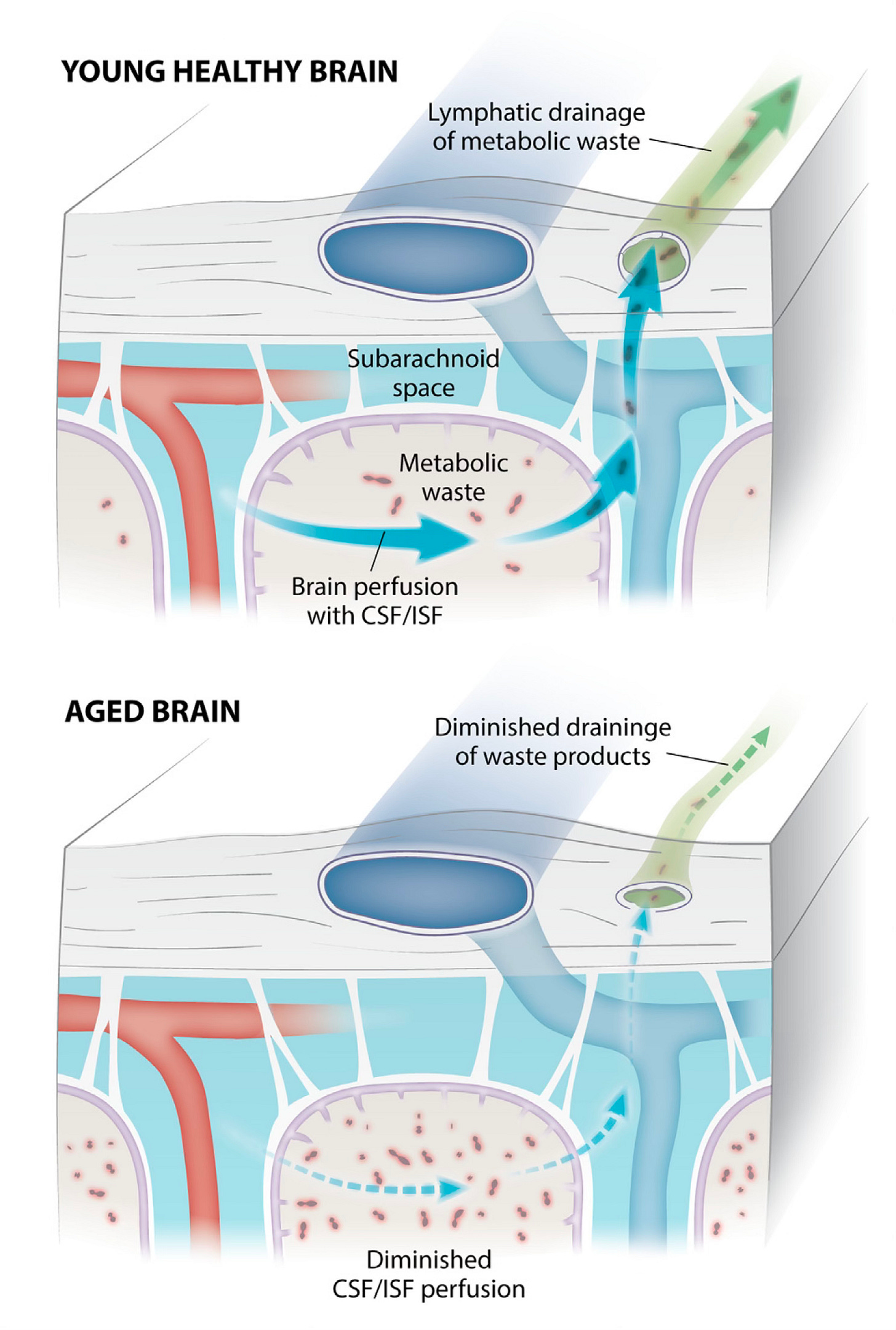
2. Clearing Brain Waste: The Glymphatic System
One of the most remarkable discoveries in neuroscience is the glymphatic system—the brain’s waste-removal network.
While you sleep:
-
Brain cells shrink slightly
-
Cerebrospinal fluid flows more freely
-
Toxins like beta-amyloid are flushed out
This cleaning process is far more active during sleep than wakefulness, helping protect the brain from long-term damage and cognitive decline.
Image caption: During sleep, cerebrospinal fluid washes through brain tissue, removing metabolic waste.
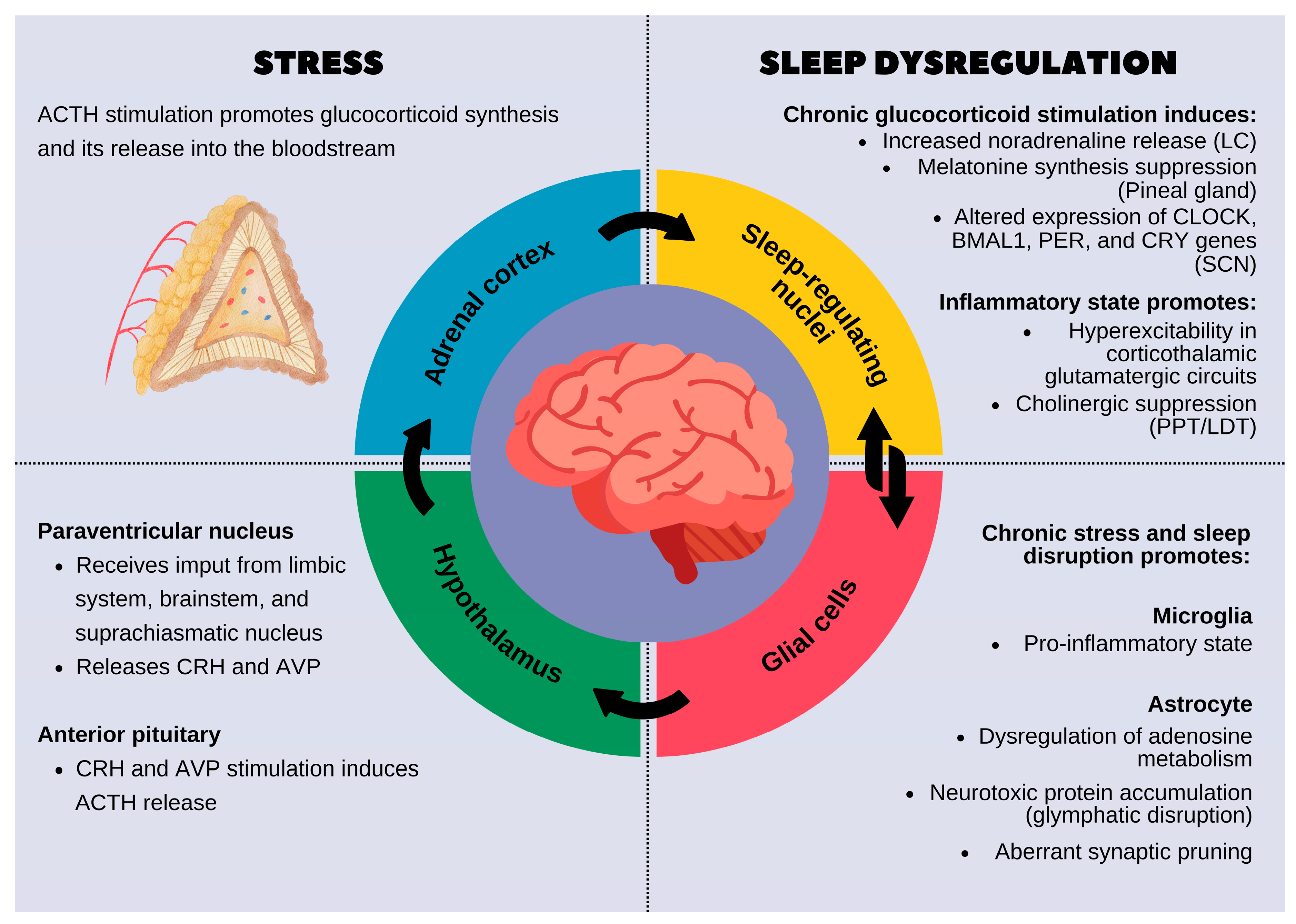
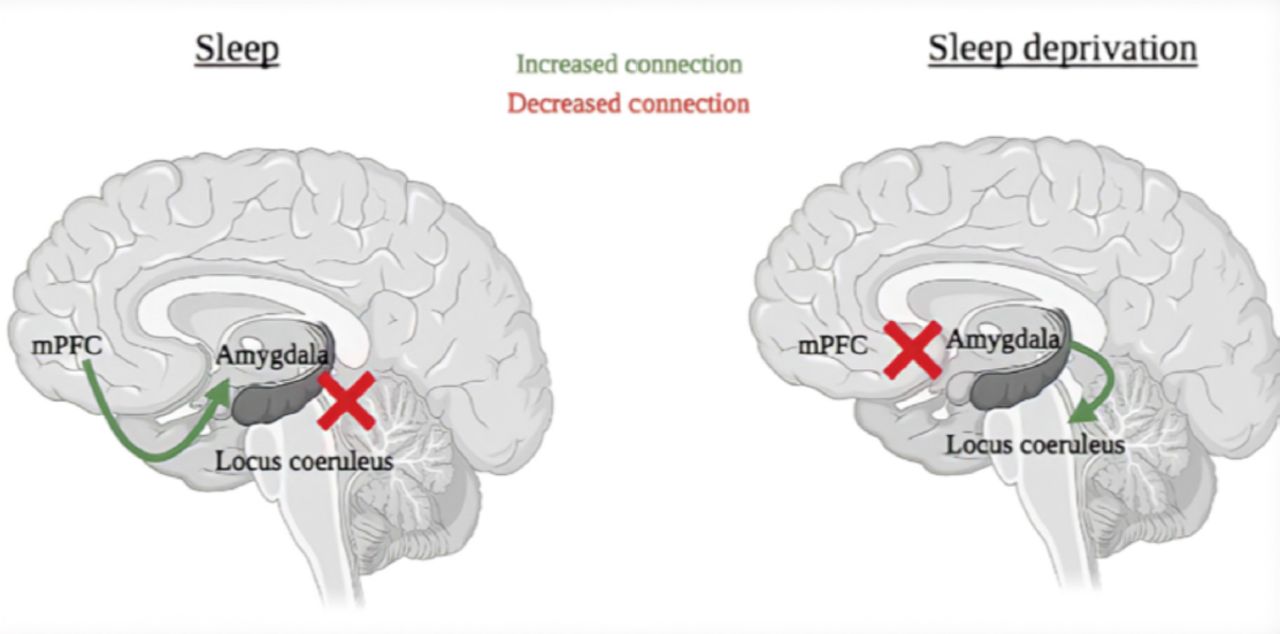
3. Repairing Stress Damage and Emotional Circuits
Chronic stress overstimulates the brain’s fear center (the amygdala) and weakens rational control from the prefrontal cortex. Sleep—especially REM sleep—helps rebalance this system.
During quality sleep:
-
Stress hormones like cortisol decrease
-
Emotional memories are processed safely
-
The brain becomes less reactive and more resilient
This is why a good night’s sleep can dramatically change how problems feel the next day.
Image caption: REM sleep helps regulate emotional responses by calming stress-related brain regions.
4. Memory Repair and Neural Rewiring
Sleep strengthens important neural connections while trimming unnecessary ones—a process called synaptic pruning.
This allows the brain to:
-
Consolidate learning and skills
-
Improve focus and decision-making
-
Enhance long-term memory storage
In recovery from addiction, trauma, or burnout, this rewiring process is critical for building healthier thought patterns.
Image caption: Sleep supports memory consolidation and reshapes neural pathways for better brain efficiency.
5. Why Sleep Is Essential for Long-Term Brain Health
Consistent, high-quality sleep supports:
-
Neuroplasticity
-
Emotional stability
-
Reduced relapse risk
-
Better impulse control
Without enough sleep, the brain remains in a constant state of low-grade injury. With sleep, it gains the chance to heal—night after night.
Image caption: Healthy sleep patterns support long-term brain repair and cognitive resilience.
Conclusion
Sleep is the brain’s natural repair laboratory. Every night of deep, restorative sleep strengthens neural circuits, clears harmful waste, and restores emotional balance. Whether recovering from stress, addiction, or mental overload, sleep is not optional—it is foundational to healing.