Rubbing, dragging, or pressing the body against the carpet is one of the clearest signals that your dog is trying to relieve discomfort, whether it’s from itching, irritation, or deeper pain.
While dogs sometimes rub for fun, repeated or intense rubbing almost always points to a skin or medical issue that needs attention.
Below is a detailed, veterinarian-style breakdown of what this behavior really means.
1️⃣ Allergic Skin Disease — The Most Common Cause of Carpet Rubbing
Allergies cause significant itchiness and inflammation, driving dogs to rub their bodies against anything textured for relief — especially carpets.
3 Major Types of Allergies That Trigger Rubbing:
• Environmental allergies (pollen, dust mites, grasses)
• Food allergies (proteins like chicken, beef, dairy, wheat)
• Contact allergies (cleaners, detergents, carpet chemicals)
What You’ll Notice:
-
Red or pink patches on belly, armpits, or thighs
-
Excessive paw licking
-
Ear infections or shaking
-
Rubbing after outdoor walks
Allergy-related rubbing often worsens seasonally, especially spring and fall.
2️⃣ Dry Skin, Dandruff & Low-Humidity Irritation
Dogs with dry, flaky skin experience a widespread itch that rubbing temporarily relieves.
Common causes of dry skin:
• Cold weather / low humidity
• Over-bathing
• Poor diet lacking omega-3 fatty acids
• Hypothyroidism
Symptoms to look for:
-
White flakes on coat
-
Rough, dull fur
-
Mild redness
-
Frequent rubbing after waking up or resting
Dry skin is often overlooked but extremely uncomfortable for dogs.
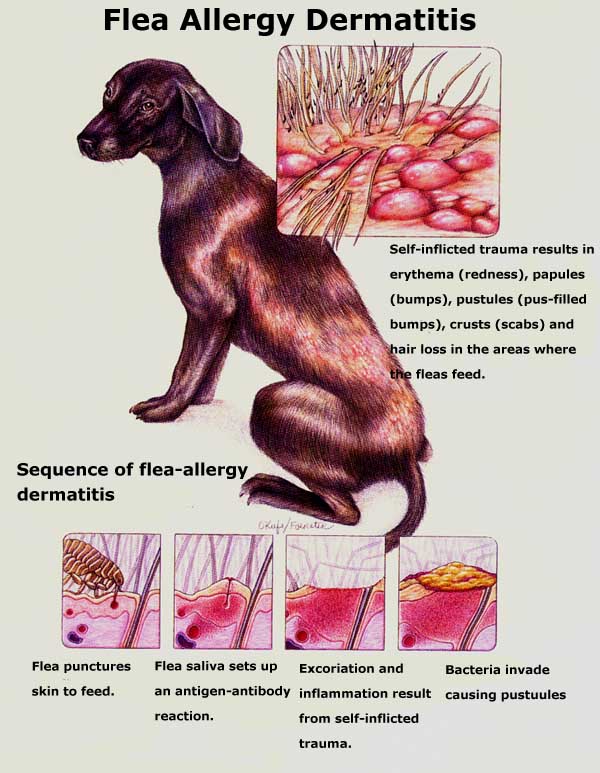
3️⃣ Parasites: Fleas, Ticks & Mites (Including Mange)
Parasites trigger intense, sudden itching, especially along the lower back, tail base, and sides.
Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD)
A single flea bite can cause extreme itching and scab formation in allergic dogs.
Mites (Demodex, Sarcoptes)
Cause severe irritation, crusting, and near-constant rubbing.
Signs parasites might be the cause:
✔ Sudden frantic rubbing
✔ Scabs or bumps over back
✔ Tail-base chewing
✔ Hair thinning in irritated areas
If rubbing becomes violent or continuous, parasites are a strong possibility.
4️⃣ Yeast or Bacterial Skin Infection
Skin infections develop when inflammation goes untreated, becoming painful and itchy.
Watch for:
-
Oily or greasy coat
-
Darkened or thickened skin
-
Musty smell (yeast)
-
Hot spots
-
Red, irritated patches
Carpet rubbing is the dog’s attempt to scratch areas that are difficult to reach.
5️⃣ Anal Gland Discomfort — The “Rear Rubbing” Cause
If the rubbing seems focused on the rear or lower back, swollen or impacted anal glands might be the culprit.
Signs of anal gland issues:
-
Scooting
-
Fishy smell
-
Excessive licking of the rear
-
Sudden rubbing after bowel movements
This condition quickly becomes painful if untreated.
6️⃣ Underlying Pain: Spine, Hips, or Muscles
Not all rubbing is itch-based — sometimes it’s an attempt to relieve pressure or pain.
Pain-related rubbing occurs with:
• Arthritis
• Hip dysplasia
• Muscle soreness
• Spinal nerve irritation
Clues it may be pain, not itch:
✔ The dog rubs slowly and repeatedly
✔ The action looks strained, not frantic
✔ Stiffness when standing up
✔ Avoiding stairs or jumping
If rubbing appears in older dogs or after exercise, consider pain as a top cause.
📌 When Is Carpet Rubbing a Red Flag?
Seek a veterinary exam if you notice:
❗ Open sores or bleeding skin
❗ Strong odor (infection)
❗ Rubbing paired with hair loss
❗ Sudden behavioral change
❗ Intensifying rubbing over days
❗ Swelling, hot spots, or crusty lesions
Persistent rubbing means ongoing skin or internal discomfort.
📌 What You Can Do at Home
✔ Wipe paws and belly after walks to reduce allergen contact
✔ Moisturize skin with hypoallergenic dog-safe sprays
✔ Add omega-3 supplements for stronger skin barrier
✔ Use sensitive-skin shampoos (oatmeal, aloe, chlorhexidine)
✔ Vacuum carpets frequently to remove dust mites
✔ Ensure year-round flea & tick prevention
If rubbing continues for more than a week, deeper diagnostics are needed.